

However, with the possibility of incidental blood contamination, intraarticular hemorrhage, or protein exudation in various inflammatory diseases, it is best to put some portion into an EDTA anticoagulant blood tube. TEST PRIORITIES FOR LESS THAN 1 ML OF SYNOVIAL FLUIDĬytology and white blood cell differential with total nucleated cell estimate and viscosity Type B cells and type A cells demonstrate immunohistochemical reactivity to heat shock protein 25 (HSP25) and CD18, respectively. 1, 2 Type A are derived from bloodborne mononuclear cells and are considered resident tissue macrophages, much like hepatic Kupffer cells ( Figure 12-1 and Figure 12-2). The type B cells, which constitute 70% to 90% of intimal cells, secrete components for tissue interstitium and synovial fluid that include collagens, fibronectin, hyaluronan, and lubricin. The intima is made-up mostly of secretory, fibroblast-related, synoviocytes (type B cell) and fewer macrophages (type A cell). The fenestrated synovial capillaries, up to 50 times more permeable to water compared with continuous capillaries, allow water and small solutes into the subintima but exclude varied proportions of albumin and larger proteins such as fibrinogen and clotting factors.Īs fluid enters and leaves the joint cavity, its diffusion and composition is regulated by connective tissue of the subintima and cells of the intima, or synovial lining.
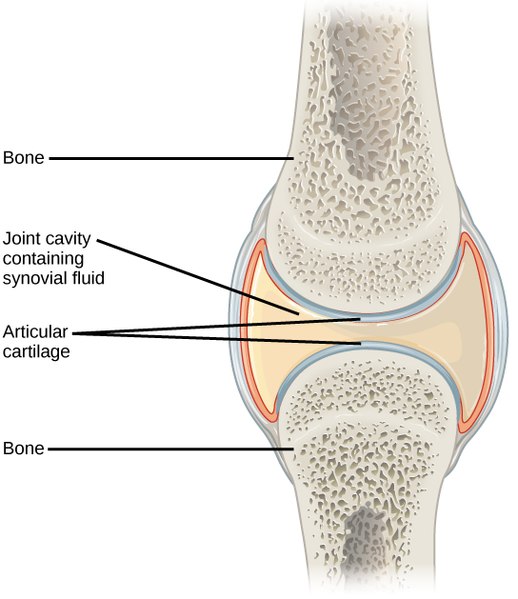
Synovium is essentially a living ultrafiltration membrane with fenestrated capillaries just below an intimal surface that contains wide intercellular gaps, but unlike true membranes, has no epithelial cells and no basement membrane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
