
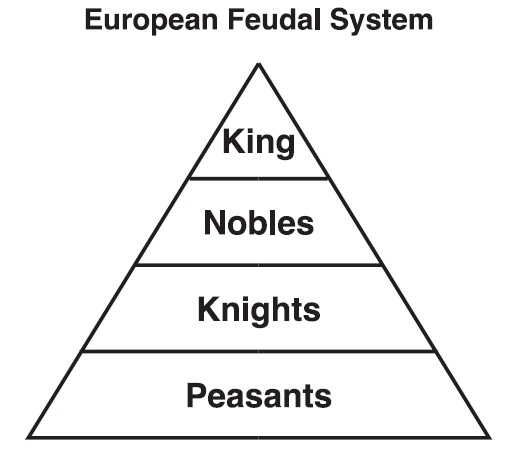
Determining lifestyle is a way to show how social classes lived their lives and how they compared to other classes. The occupation and job of a person in different social classes can affect how the people lived and spent their time, showing their status and role in society. This differed from one class to another greatly with popes and kings having the most power and peasants having the least. In the Dark Ages, authority and power can show how people interacted and who medieval citizens looked up to, which can definitely show how social classes can have traits that are unlike. To tell the differences between people in different social classes, historians look to the different roles and lifestyles that people had. Feudalism was a very intelligent way for medieval people to accomplish tasks and finish jobs through the Dark Ages. This loss of population caused a change in how feudalism could be used since there were not as many people to take place in it and all people were focused on a cure to the plague. During this era, the Black Death was sweeping across Europe and killing much of the population. Feudalism eventually ended in the 1400s AD. Due to this, many communities split into small villages and worked together within the isolated village to form feudalism. At this time, barbarian attacks were plaguing Europe, the Roman Empire had recently fallen, and the governments were falling apart. The Early Middle Ages began around the 500s AD. The system of feudalism stemmed from the fall of the Roman Empire and Europe. In feudalism, nobles owned land that knights guarded and peasants worked ("How Did the Social Structure During the Middle Ages Reflect the Worldview of the Time?"). Another interaction between social classes is one called feudalism. For example, nobles, knights, and peasants swore an oath to the king for protection, an agreement known as a vassal. These classes did work together in many ways. Peasants spent most of their time working at the lord's manor ("Medieval Social Classes"). This class made up 90% of Europe's population at the time. The lowest class during the Middle Ages consisted of peasants, also known as serfs. They were armored warriors who protected the lord's land called the manor. The next social class down during the Middle Ages included knights. Nobles, also known as lords, were next on the social pyramid (meaning that they had less power than royalty and popes) and were wealthy landowners in Medieval Europe. Below the pope was royalty who ruled separate kingdoms. The pope was the leader of the Roman Catholic Church and had more power and wealth than any other parts of society. In Medieval Europe, there were five main social classes. In any civilization in history, one of the most essential factors in human interactions is the status a person finds themselves in, called a social class.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
